Front End Development Landscape
13 Apr 2018
Over the last few years, I’ve helped lots of developers build web applications on various platforms including GE’s Predix. Many of these developers are not actually “web” developers. They’re Java developers building services, data scientists writing algorithms, or mechanical engineers that just want to see their data on a web app. This post covers a wide variety of front end development concepts intended to make these folks comfortable and productive.
Basic Technology
Before diving into specifics, it’s important to understand the basic building blocks of the web.
- Browser: The web browser is arguably the most popular, powerful piece of software in the world. At its core, the browser can fetch resources, render UI elements, apply visual style to the elements, and execute scripts. Modern browsers such as Chrome and Firefox are constantly evolving to implement the latest specs from the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
- Communication Protocols
- HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol is a stateless application-layer communication protocol for transmitting documents. MIME type headers tell browsers how to handle various document types. HTTP has served us well for over 20 years, but each request requires the overhead of a “handshake”, so newer streaming technologies such as HTTP/2 and Websockets are becoming more popular.
- WebSocket is a full-duplex streaming protocol over a single TCP connection. Works on the same ports as HTTP. (80 and 443)
- HTTP/2 is a major revision of the HTTP protocol, which allows streaming multiple files over a single connection, and pushing data from client to server.
- HTML Hypertext Markup Language is a simple formatting language used to structure content.
- The Document Object Model, or DOM is a programming interface for HTML and XML documents that’s implemented by the browser. Developers can manipulate these documents by calling the DOM API from front end JavaScript code.
- CSS Cascading Stylesheets is a language used to style and layout content. (colors, fonts, etc.)
- JavaScript is a lightweight interpreted programming language that can be used to implement complex features in various environments, including web browsers and servers.
- ES6 is 6th edition of Javascript. It’s officially called ECMAScript2015. It addresses ugly warts in earlier versions of the language, and introduces many powerful new features. It’s now supported by all current browsers and NodeJS.
- JSON - Javascript Object Notation is the format for serializing JavaScript objects. Due to its simplicity, it has become a popular format for data transmission.
- Related languages Many languages have been created to compile to JavaScript. The goal is to increase developer productivity, and produce code that can be run everywhere JS is supported. Typescript from Microsoft is one popular example.
- REST REpresentational State Transfer is an architectural pattern for distributed systems. Although not strictly defined as part of the pattern, REST usually implies JSON over HTTP.
Web Application Essentials
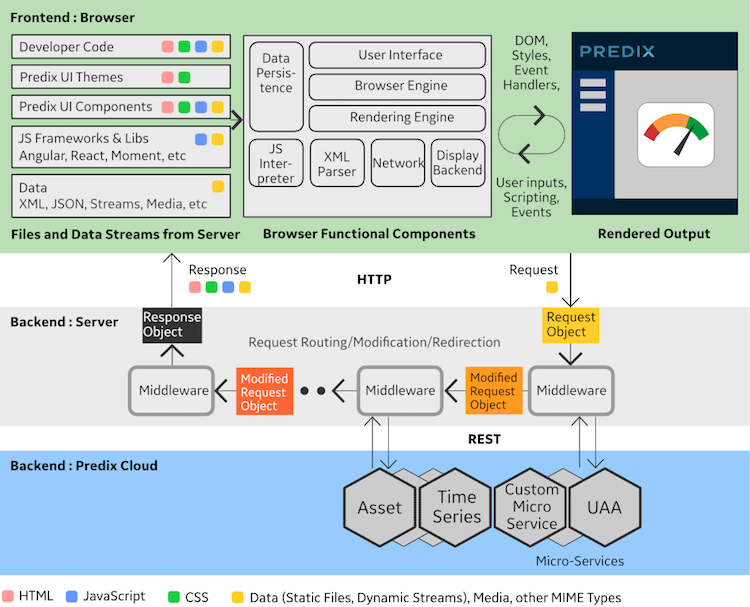
Browser Layer
The bulk of a front end application is user interface code, which runs in the web browser. As browsers have become more powerful, this area has expanded and grown in complexity. These concepts and building blocks can be used to build a modern front end application.
- JavaScript Frameworks - define the entire design of a front end application design. With the rise of Single Page Apps, these have become more popular. Although not required, frameworks can help create production quality apps more quickly, and can help front end dev teams work together more efficiently.
- Common features
- Design patterns - Encourage developers to follow patterns such as Model-View-Controller (MVC), Inversion-of-control (IOC), PRPL etc.
- URL routing - Respond to changes in the browser address bar. Instead of loading a new file as in traditional multi-page web sites, different action can be taken such as making an API call, or loading a UI component onto the page.
- Data binding - Display data from the model in the UI view. Two-way data binding means that user changes to data in the UI are also persisted to the model.
- State management - Store and retrieve UI state from various UI components.
- Templates - Layout templates with placeholders for model data. Handlebars is one example.
- Event handling - Provide consistent way to handle events from user interaction or back end service responses.
- CLI - Many frameworks provide a command line interface to help developers. These can provide project scaffolding, build tooling, local development server, and more.
- API calls - Provide a standard method for calling services and handling responses.
- Examples: Vue, Angular, Ember, Backbone
- Common features
- Javascript Libraries are packages of code that get called by an application to perform a task. Here are a few examples.
- Polymer is a JS library that simplifies creation of web components, and allows them to run in older browsers.
- React is a very popular library for building UI using custom elements, and an XML based DSL.
- Moment “Parse, validate, manipulate, and display dates and times”
- D3 allows you to build complex data driven visualizations.
- CSS Frameworks - allow you to quickly and easily apply consistent styles to build a responsive web application. Some may contain JS for advanced interactive components. Some examples include: Bootstrap from Twitter, Foundation, and Inuit. (Predix design system uses Inuit.)
- Persistence - Some data can be stored in the browser, using the
localStorageAPI or cookies. Cookies are tiny pieces of data stored in the browser, and are sent with every request to the web server. These are typically used for session management. - Web Components are custom, reusable, encapsulated tags based on web standards. They can be used along with most of the major frameworks: https://custom-elements-everywhere.com/. Publicly available web components are produced by many people and organizations including Google, Vaadin, and GE.
- Progressive Web Apps “Use modern web capabilities to deliver an app-like user experience.” For example, a PWA could support offline use, or native mobile features such as GPS, camera, etc.
Server Layer
No front end application can function without a server to provide source files to the browser. In essence, the web server simply maps requested URLs to files, and returns those files to the browser. Today’s web servers also perform many more functions.
- Web server common features
- HTTP server is software that understands URLs and HTTP and delivers content to a browser.
- Static content - includes HTML, CSS, JS and images.
- Authentication - logic for identifying users should be done on the server, since browser code is inherently insecure. Web servers can perform simple authentication, or integrated with an identity server.
- Caching - content can be stored in memory to improve performance
- Compression - most servers compress content using gzip before sending it over the wire to a user. Browsers automatically expand the content.
- Redirects - servers can send a “redirect” response to a browser’s request. This tells the browser to make a new request to a different URL.
- Session - specific user information can be stored in the web server, or a caching server such as redis.
- Examples: nginx, apache
- Application servers support the common web server features above, as well as more dynamic features.
- Scripting languages can be used on the fly to generate HTML. Examples are JSP, ASP, PHP.
- Templates can be used to generate dynamic HTML. This can be done in the browser or server layer, depending on the application.
- Proxy - A very important concept is proxying user requests from the browser, through the application server, to separate back end services. This is a recommended pattern to improve security and testability.
- Service integration - servers can be configured with credentials to access secure databases and APIs.
- Examples: Express, Ruby on Rails, IIS, Tomcat
- Web sockets - web servers may also serve as web socket servers to deliver streaming data to an end user. Sockets provide data closer to real time with less overhead. A web socket server may be a separate server or a plug in to a web server.
- HTTP server is software that understands URLs and HTTP and delivers content to a browser.
Development Tools & Concepts
The wide array of tools for front end development can seem overwhelming. Understanding the major development tasks and concepts helps simplify the situation.
- Node.js is a JavaScript runtime that supports the majority of front end dev tools. Node.js can run on hosted servers to support web applications or APIS. And developers use node on laptops to run a wide variety of dev tools. Since front end devs are familiar with JS, they’re comfortable running JS locally to run dev tools and build new tools.
- Package Managers are used in most modern programming languages. (Maven, Pip, Gem, etc.) Most front end applications use these tools:
- NPM - the Node Package Manager is the most popular package manager for front end work. NPM is used to install most of the dev tools listed here, web servers and server packages, and sometimes front end packages from a global package registry.
- Bower is used to install browser code into the application under construction. It was created by Twitter, and was quite popular, but it has now been deprecated.
- Yarn is a newer package manager which installs packages from the npm registry, and provides benefits such as improved speed and deterministic installs.
- Task runners are used to chain together all the various pieces of the front end app build & deployment pipeline. Developers use task runners in their daily workflow, and the task runners in turn use many other plugins for pre-processing, testing, etc.
- Gulp is a toolkit for automating dev & build processes. It’s used by the Predix Webapp Starter.
- Grunt is a slightly older, but similar tool.
- Pre-processors are used to optimize application code for deployment.
- Transpilers - transform code from one language to another. For the web, the target language is JavaScript. Source language may be typescript, coffeescript or others. Babel is the most common transpiler, and it’s used under the hood by the Predix Web App Starter
- CSS Pre-processors - Are used to transform advanced stylesheet languages into basic CSS for display in the browser. Examples include sass, less, and stylus.
- Bundlers - are used to improve web application performance. Making large numbers of requests for small files from browser to server causes slow page loading. So bundlers are used to concatenate and sometimes compress small files into large files. This way an entire application can be served in just a few fragments or “shards”. Webpack is the most common bundler today.
- Linters such as ESLint are used to scan code and make sure there are no syntax errors, and to enforce code style rules. This especially important since JS is not a compiled language. Linters can be integrated into code editors to instantly highlight errors as the developer types.
- Testing should be performed at various levels of a front end application. Some tests can be performed in Node.js, while some must be performed in the browser.
- Unit tests are small fast tests that exercise low level functions with no dependencies. These can run in Node.js.
- UI Component testing - Developers can test a web component in isolation using tools such as Web Component Tester.
- UI Application testing is critical, for testing the entire application in a browser. The UI could be tested alone with mock services, or end-to-end tests could be run with live services. Tests can be run on a deverloper’s machine, or in the cloud using a service such as Sauce Labs.
- WebDriver is an interface that enables driving a browser from test code. There are many implementations in various languages.
- Selenium is a tool that drives the browser, and listens for commands from WebDriver code.
- Framework CLIs - Many of the modern front end frameworks provide their own CLI tools for scaffolding, tooling, local server, etc. Examples include: React, Polymer, angular, and ember.
- There are many code editors and IDEs that work well for front end development. WebStorm is the best full featured IDE, but requires a license fee. Visual Studio Code is the best free editor. There are many plugins available for highlighting, linting, etc.
- Debugging front end code is easy with modern browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, and Safari. These browsers provide a “Developer” menu option that supports DOM element debugging, script debugging with breakpoints, performance testing, and more.
Mobile
Many people today use mobile devices to interact with internet applications. There are a few major categories of mobile apps, each with their own tools & patterns.
- Apple iOS is one of the top two mobile operating systems.
- Swift is the modern language used to build native iOS applications. Native apps have full access to all the device hardware. (GPS, camera, etc.) Objective-C is an older alternative language.
- XCode is Apple’s IDE for mobile development. It runs only on Apple hardware.
- iOS Apps are distributed through the Apple App Store, or a private “enterprise” store. There aretandards for apps being accepted to the Apple App Store which must be met.
- Android from Google is the other top mobile OS.
- Native applications are written in Java or Kotlin.
- Android Studio is the IDE used for Android development. It can run on Windows, Mac or Linux.
- Android apps are more easily distributed through the Google Play Store, or a private store.
- Mobile Web applications are simply web applications that are designed to run on a small screen.
- Responsive design is the term used to describe an app that has been designed to run on a variety of screen sizes. The app will “respond” appropriately, showing less content on a smaller device.
- No application code is required to be installed on a user’s device, since the app runs in the mobile browser.
- A mobile web app may be the same codebase as desktop web app, if the code is responsive.
- Hybrid - is a cross between a native app and a mobile web app. In this case, a simple “shell” application is distributed through the app store. This native shell application has minimal functionality, and provides a “web view” component which displays a mobile web application or mobile web components. The benefit of a Hybrid app is that most of the web app code can be shared across both iOS and Android.
- Cross platform - Tools can be used to convert a standard web application (HTML, JS, CSS) into native code that’s compiled and distributed through an app store. This allows a single code base to support both iOS and Android, although access to some device hardware may be limited. Examples include:
References
- https://frontendmasters.com/books/front-end-handbook/2017/
- https://www.predix.io/resources/tutorials/tutorial-details.html?tutorial_id=2101
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Henry Navarro for creating the diagram.